Digital health
Digital health
Wireless devices, hardware as well as software sensors, microprocessors and other integrated circuits, the internet, social networking mobile, health IT, genomics and personal genetic information are all essential components of digital health applications.
Patient
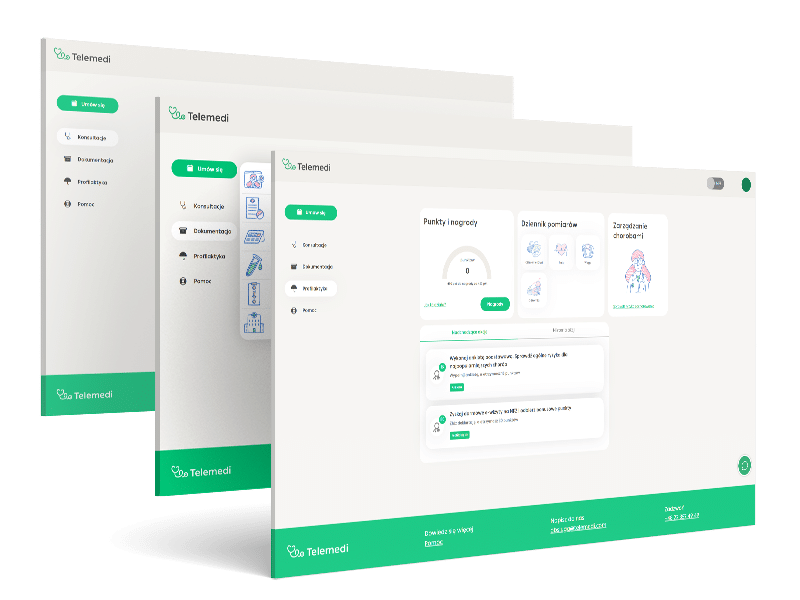
Why digital health is important?
Medical digital health employs more than just technology and tool according to Deloitte Insights. Additionally, it considers “radically interoperable data, artificial intelligence (AI) and open, secure platforms to be central to the promise of more consumer-focused, prevention-oriented care” to be at the heart of the initiative.
Digital health technologies continue to undergo significant transformations as a result of advancements of AI, big data, robotics, and machine learning. In addition, developments in ingestible sensors, robotic caregivers, devices and apps for remote patient monitoring continue to evolve in response to shifts in the digital healthcare landscape.
Deloitte claims that AI will speed up the development of new diseases-fighting therapies and vaccines, enabling major scientific breakthroughs. Consumers will be empowered to prevent health issues from arising through personalized recommendations and digital therapeutics that are enabled by AI.
Diagnoses and treatments in health systems will be influenced by artificial intelligence-generated insights, which will make them safer and more effective.
Additionally, intelligent manufacturing and supply chain solutions will guarantee, that the patients receive the appropriate treatments conditions and interventions at precisely the right time.
In its infancy, eHealth referred to the integration of ICT (Information and Communications Technology) and electronic processes across all aspects of health and care.

Digital health technology examples
Innovations in the digital health aim to save time, improve accuracy and efficiency and combine technologies in novel ways for healthcare.mHealth, IoT (Internet of Things), medicine and augmented reality (AR), blockchain and electronic medical records (EMRs). These innovations may combine them.
The combination of medical devices and applications that connect to health IT systems, that make use of networking technologies is referred to as the “internet of medical things” (IoMT).
The Internet of Things can be used in a variety of ways, from telemedicine technology to smart sensor technologies, that can collect data at the user level to reduce the likelihood of contracting infectious diseases and improve communication between patients and healhcare professionals. For instance, as more providers turned to technology and provided virtual services to patients, demand for telehealth services increased in response to the COVID-19.
There are always the new IoT applications for healthcare. Smartphone-based pacemaker devices were named the top innovation for 2021 by Cleveland Clinic. Pacemaker devices, that are connected to smartphones can be made to securely and wirelessly transmit data to a patient’s network by using an app on mobile medical device.
Who are Patients?
ePatients are healthcare consumers who actively engage in and participate in their own health and care. They know everything there is to know about their health and the healthcare sector. They may be involved in their health and care as well as the care of those they care for. The word “e” can mean: “electronic”, “equipped”, “enabled”, “engaged”, “equal” and other related terms, in contrast to eHealth.
Health Information Technology
At its most fundamental level, health information technology (HIT) is the application of information technology to health and healthcare. In other words, it facilitates the secure exchange of digital health information between patients, healthcare providers and various other stakeholders in health and care as well as the management of digital health information across computerized systems.
Mobile healthcare (mHealth)
eHealth’s area of mobile health technology uses mobile communication devices to deliver health services and information. Utilizing mobile devices to collect community and clinical health data, providing patients, health care providers and researchers with health and care information, real-time patients monitoring and direct care are all examples of applications.
Precision Personalized Medicine
Accuracy medication suggests that an individual’s well-being and mind ought to be customizable with clinical choices, practices and items being customized for the singular patient. Precision medicine, another name for personalized care, divides patients into groups based on their likelihood of developing an illness or how well they respond to treatment conditions.
Telehealth
Telehealth involves the delivery of services and information related to healthcare that support health education, administrative tasks and patients healthcare through the use of telecommunications technologies.
It includes a wide range of quality services, from the interaction between patients and clinicians and care of patient’ s education, advice to intervention and monitoring. Digital technologies are not always involved.
Telemedicine
The term “telemedicine” refers to the process by which a patient’s health is improved by transferring medical data electronically from one location to another. It is mostly thought of as a clinical tool that is used to provide the remote clinical health care rather than support for patients or administrative professionals.
It makes use of both: analog and digital technologies, just like telehealth.
Quantified self tracking digital healthcare
It refers to a person who is tracking their own biological, physical, behavioral or environmental data. Weight, energy level, mood, time spent, quality of sleep, cognitive performance, exercise and health are all tracked and analyzed with this self-tracking using wearable medical devices. It can help make it possible for users to quantify biometrics, that was previously unknown, saving time and money.
Functionalities

Dedicated accounts for the doctor, patient, and administrator

Electronic medical documentation and e-prescriptions

Collection of medical data, generation of reports, administration of system users

3 communication channels – chat, video and phone call

Platform supported by AI & Machine Learning

HIPAA & GDPR compliance
Advantages
Cost reduced by up to 60% per visit
Improved coverage in rural regions and small towns
Global coverage with various languages
Increased revenue and customers base
Improved availability to GPs and specialists, 24/7 service
Improved customers satisfaction, online consultations rated 4.8/5
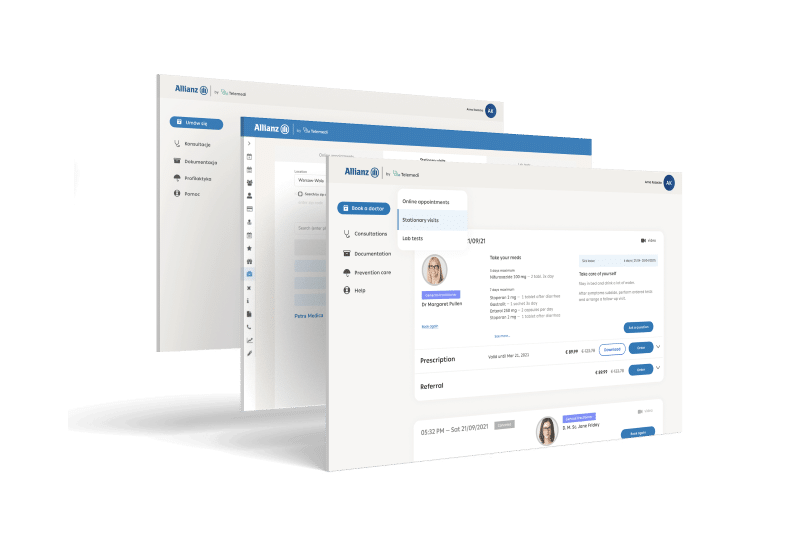
Integrated digital health solution
Telemedi platform can be used in various
business models with API integration, especially
between data, applications and devices
Let’s meet
Leave your details in the form below and lets talk!
Let’s talk about how to blend digital health with traditional healthcare efficiently.
Paweł Sieczkiewicz
CEO
Telemedi
"*" indicates required fields